Are you worried about atherosclerosis? Here’s what you need to know.
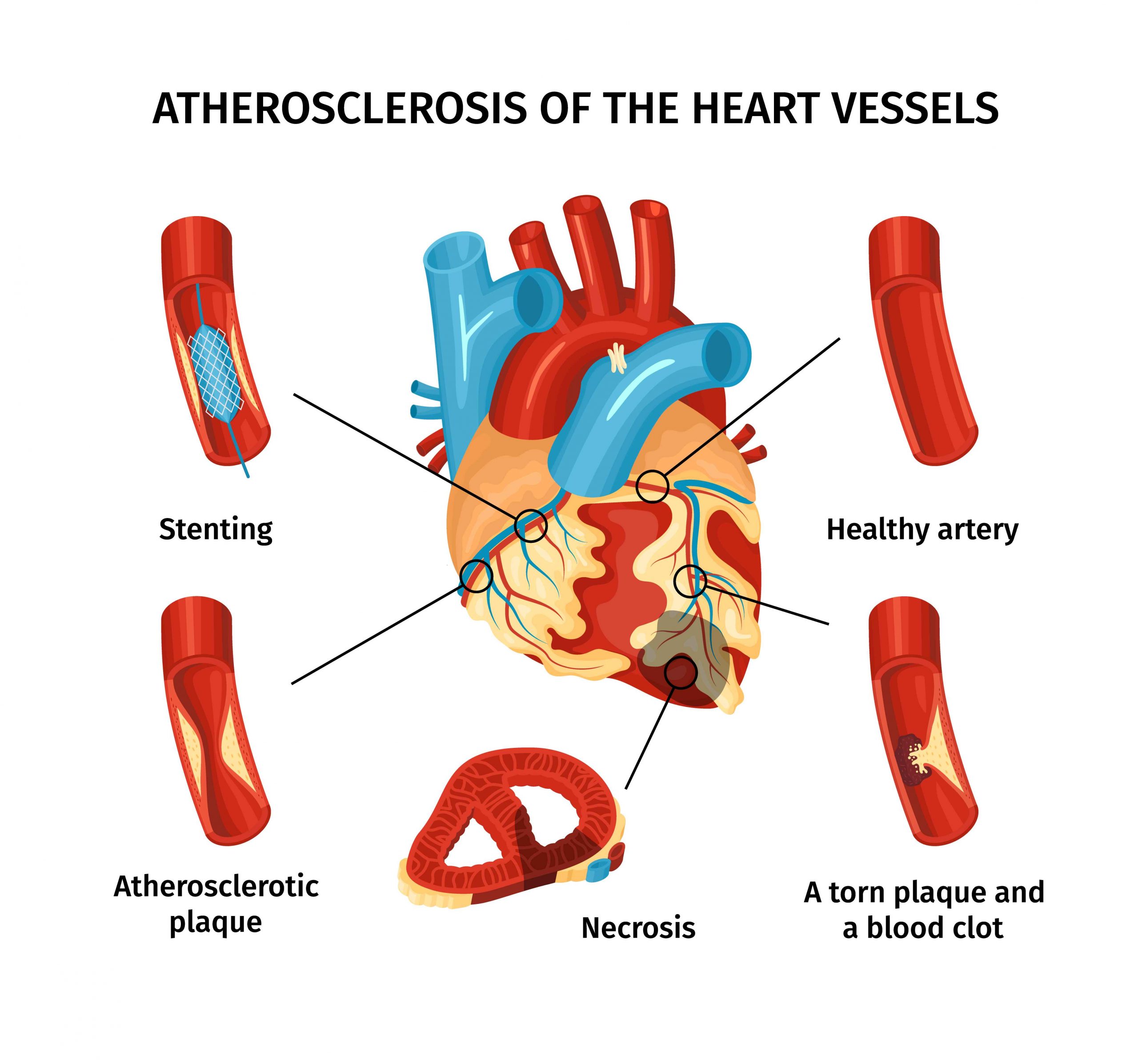
Atherosclerosis is a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, blocking blood flow. This can lead to serious health issues like heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Understanding the causes, risks, and treatment options for atherosclerosis is crucial to preventing these complications and maintaining heart health.
What Is Atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis occurs when cholesterol, fat, and other substances accumulate inside the arteries. These deposits, called plaque, cause the arteries to narrow and harden. The reduced blood flow can lead to dangerous health problems such as:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Peripheral artery disease
- Aneurysms
Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis
Certain factors increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis. These include:
- Age: The risk increases with age.
- Family history: A family history of heart disease or stroke can raise your risk.
- High blood pressure: This can damage arteries, leading to plaque buildup.
- High cholesterol levels: High LDL (bad) cholesterol levels contribute to plaque formation.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels.
- Smoking: Smoking accelerates plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can increase cholesterol and blood pressure.
Symptoms of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis often develops slowly without noticeable symptoms. As plaque builds up, you may experience:
- Chest pain (angina): This occurs when the heart doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood.
- Shortness of breath: Reduced blood flow makes it harder for the body to get oxygen.
- Weakness or numbness in limbs: Atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to the arms or legs can cause this.
- Vision problems: Blocked arteries in the eyes can lead to vision changes.
How Doctors Diagnose Atherosclerosis
Doctors can detect atherosclerosis through routine exams and tests. They may check your pulse and blood pressure. Blood tests will also measure cholesterol and glucose levels. If needed, your doctor might suggest:
- Ultrasound: To check blood flow and detect blockages.
- Angiogram: A dye is injected into your bloodstream, and X-rays are used to see the arteries.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This records the heart’s electrical activity to detect irregularities.
Treatment Options for Atherosclerosis
While there is no cure for atherosclerosis, treatments can help manage the condition. Treatment options include:
- Medications: Statins, blood thinners, and drugs to manage blood pressure or diabetes.
- Lifestyle changes: These are essential in managing atherosclerosis and improving heart health.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Atherosclerosis
Making the following changes to your lifestyle can slow the progression of atherosclerosis:
- Quit smoking: Smoking cessation is one of the most effective ways to reduce plaque buildup.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity improves blood circulation and lowers cholesterol.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet: Focus on vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Manage stress: Techniques like yoga and meditation can reduce stress and improve heart health.
Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
In some cases, surgery may be required to treat atherosclerosis. Procedures include:
- Angioplasty: A balloon is used to open blocked arteries, often followed by the placement of a stent to keep the artery open.
- Bypass surgery: This involves rerouting blood around blocked arteries to restore proper blood flow.
Conclusion
Atherosclerosis is a serious but manageable condition. By understanding its risks and symptoms, you can take steps to prevent its progression. If you have risk factors, talk to your doctor about preventive measures and treatment options to protect your heart health.
For More Information, Click here.


