Understanding PCOS: What You Need to Know About Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis
Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Introduction
As you enter puberty, hormonal changes significantly affect your feelings and overall well-being. Therefore, achieving a balance is crucial. However, when hormonal imbalances occur, complications such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can arise. This common hormonal disorder affects many women of reproductive age. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and diagnostic methods, you can effectively manage this condition.
Symptoms of PCOS
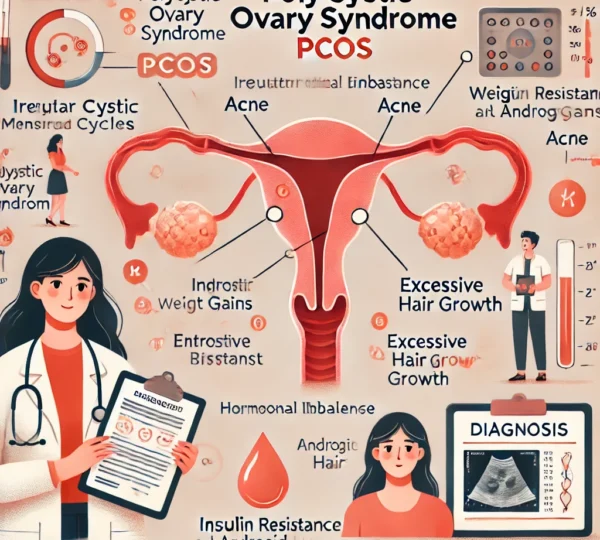
PCOS manifests in various ways, with symptoms that can differ from person to person. Common symptoms include:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Many women experience infrequent or prolonged menstrual periods, which can be frustrating.
- Excessive Hair Growth (Hirsutism): Unwanted hair growth on the face and body often causes emotional distress and can impact self-esteem.
- Acne and Oily Skin: Hormonal imbalances frequently trigger acne outbreaks and increase oil production, leading to skin issues.
- Weight Gain: Many women with PCOS struggle with weight management, making it challenging to lose weight despite efforts.
- Difficulty Getting Pregnant: Irregular ovulation often leads to challenges in conceiving, which is a significant concern for many women with PCOS.
Causes of PCOS
Researchers have not fully understood the exact cause of PCOS. However, a combination of genetic and environmental factors likely contributes to its development. Some key factors include:
- Insulin Resistance: When the body’s cells fail to respond effectively to insulin, it leads to higher insulin levels in the blood. This condition is often associated with PCOS.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) disrupt ovulation and contribute to many symptoms of PCOS.
- Genetic Factors: Additionally, a family history of PCOS increases the risk of developing the condition, suggesting a hereditary component.
Diagnosis of PCOS
To diagnose PCOS, doctors typically follow several steps:
- Medical History: Your doctor will inquire about your menstrual cycles, symptoms, and family history of hormonal disorders. This information is essential for accurate diagnosis.
- Physical Examination: They may perform a pelvic exam to check for abnormalities in the reproductive organs, helping to rule out other issues.
- Blood Tests: These tests measure hormone levels, including testosterone, estrogen, and insulin. These measurements help identify hormonal imbalances.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, doctors may conduct an ultrasound to examine the ovaries for cysts and assess their size and number.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PCOS represents a complex condition that significantly impacts a woman’s health and well-being. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and diagnostic methods, you can collaborate with your healthcare provider to create a personalized treatment plan that addresses your individual needs. With appropriate management, women with PCOS can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
To seek medical advice, always consult a Doctor. Here are our recommended experts. Click here
To read more on Women’s Health . Click Here