Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma: Understanding the Connection
Introduction: Allergic rhinitis and asthma are two common respiratory conditions that often go hand in hand. Understanding the connection between these two conditions is crucial for managing symptoms effectively. Let’s delve into how they are related and what steps you can take to keep them under control.
Understanding Allergic Rhinitis:
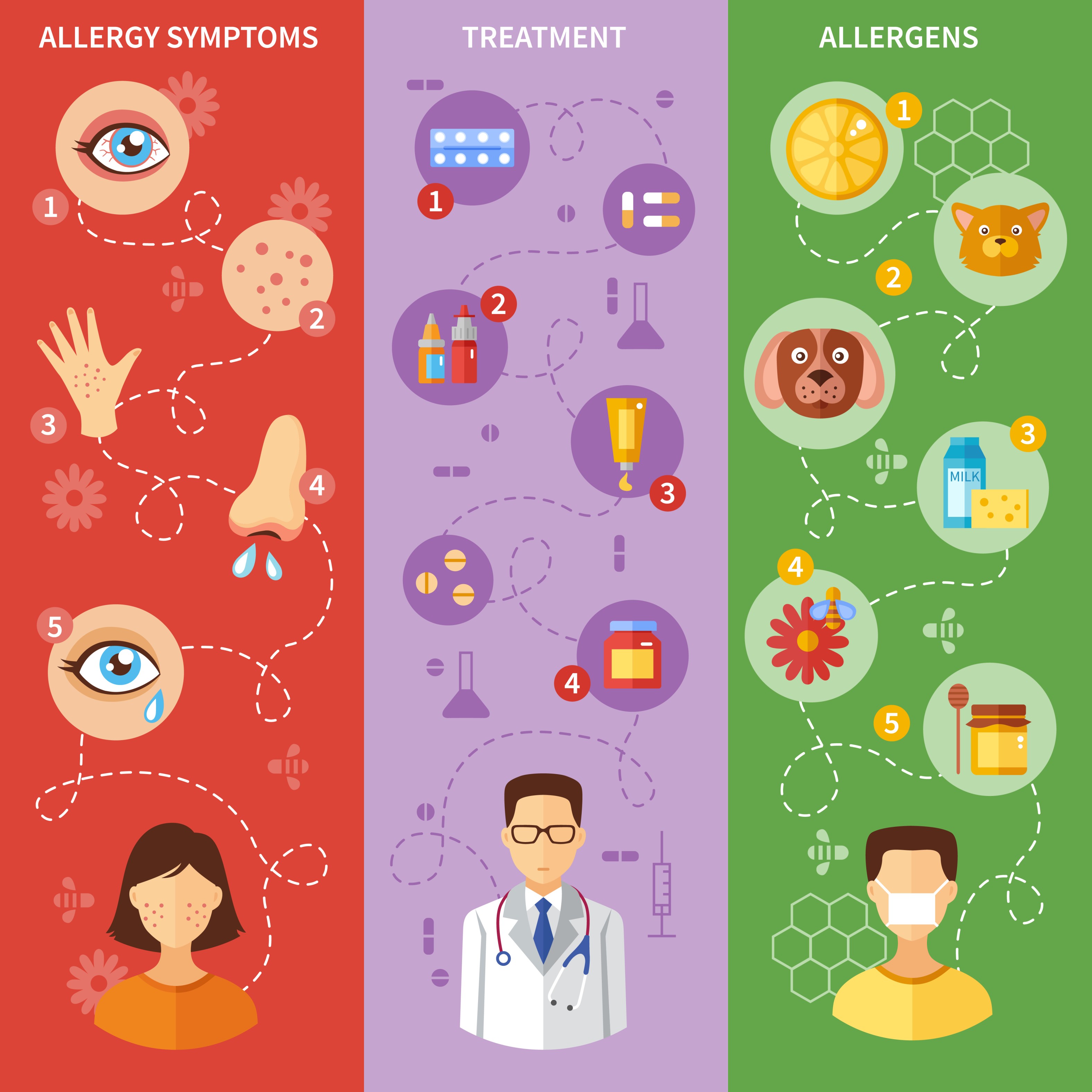
Allergic rhinitis, commonly known as hay fever, occurs when the immune system reacts to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander. Symptoms include sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itching in the eyes, nose, or throat, and watery eyes.
Understanding Asthma:
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing, wheezing, coughing, and tightness in the chest. While the exact cause of asthma is unknown, it can be triggered by various factors, including allergens, respiratory infections, and environmental factors.
The Connection Between Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma:
Many individuals with allergic rhinitis also have asthma, and vice versa. This is because the same allergens that trigger allergic rhinitis symptoms can also exacerbate asthma symptoms. When allergens enter the airways, they can cause inflammation and tightening of the muscles around the airways, making it difficult to breathe.
Additionally, allergic rhinitis can lead to nasal congestion and postnasal drip, which can aggravate asthma symptoms by triggering coughing and wheezing. Conversely, poorly controlled asthma can worsen allergic rhinitis symptoms by causing nasal inflammation and congestion.
Managing Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma:
Managing both allergic rhinitis and asthma involves a combination of prevention strategies and medication management:
- Identify and Avoid Triggers: Work with your healthcare provider to identify the allergens that trigger your symptoms and take steps to minimize exposure to them.
- Medication: Take prescribed medications as directed to control both allergic rhinitis and asthma symptoms. This may include antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Allergy Shots (Immunotherapy): In some cases, allergy shots may be recommended to help desensitize the immune system to specific allergens, reducing allergic reactions over time.
- Maintain Good Indoor Air Quality: Keep indoor air clean by using air purifiers, regularly vacuuming and dusting, and keeping windows closed during high pollen seasons.
- Follow Asthma Action Plan: If you have asthma, work with your healthcare provider to develop an asthma action plan outlining steps to take in case of worsening symptoms or an asthma attack.
Conclusion:
Understanding the connection between allergic rhinitis and asthma is essential for effectively managing both conditions. By identifying triggers, taking prescribed medications, and following preventive measures, individuals can better control their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
To seek medical advice, always consult a Doctor. Here are our recommended experts. Click here
To read more on Respiratory disease . Click Here


