Different Types of Pneumonia: Viral, Bacterial, and Fungal
Introduction:
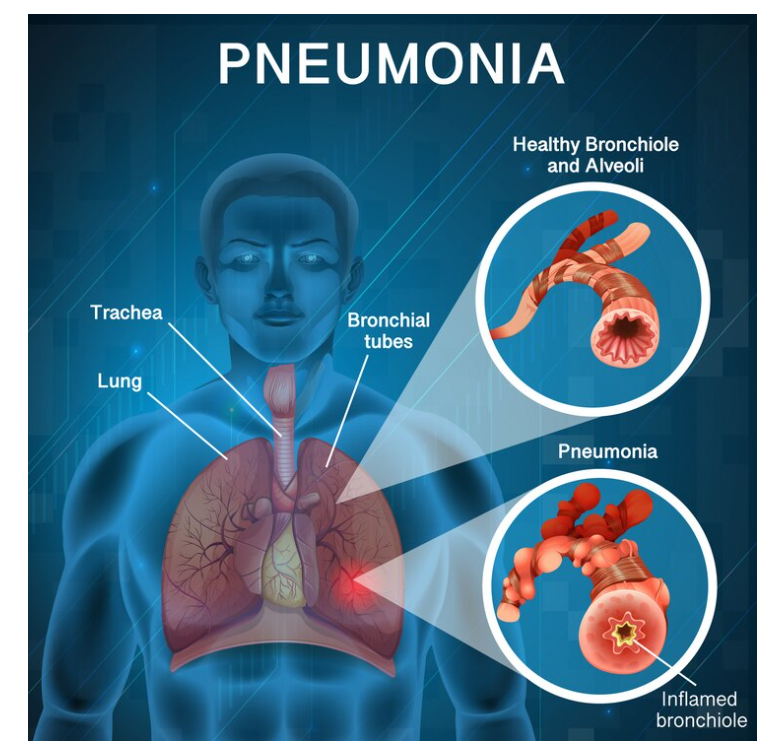
Pneumonia is not just one illness; it comes in different forms, each caused by various germs. Understanding the different types of pneumonia is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Let’s explore the distinctions between viral, bacterial, and fungal pneumonia.
Viral Pneumonia:
Viral pneumonia is caused by viruses such as influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and adenovirus. It’s often milder than bacterial pneumonia but can still cause severe symptoms, especially in young children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems. Symptoms include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.
Bacterial Pneumonia:
Bacterial pneumonia is most commonly caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae, although other bacteria can also be responsible. It tends to be more severe than viral pneumonia and can lead to complications if not treated promptly. Symptoms include high fever, productive cough with green or yellow mucus, and chest pain.
Fungal Pneumonia:
Fungal pneumonia is caused by fungi such as Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus. It primarily affects individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy. Fungal pneumonia can be challenging to diagnose and treat and may require antifungal medications. Symptoms include fever, cough, and shortness of breath.
Treatment:
Treatment for pneumonia varies depending on the type and severity of the infection. Viral pneumonia is typically managed with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms. Bacterial pneumonia requires antibiotics, while fungal pneumonia may necessitate antifungal medications. Supportive care, such as oxygen therapy, may also be provided to help with breathing.
Conclusion:
Understanding the different types of pneumonia is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Whether it’s viral, bacterial, or fungal pneumonia, seeking medical attention promptly and following the prescribed treatment plan can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
To seek medical advice, always consult a Doctor. Here are our recommended experts. Click here
To read more on Respiratory disease . Click Here



