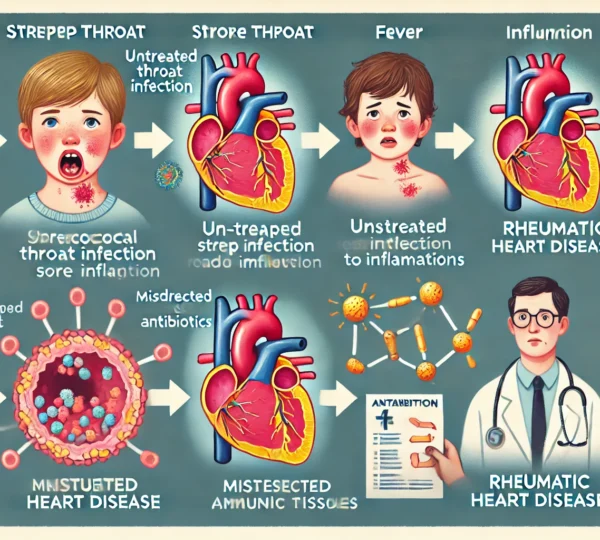
The Link Between Streptococcal Infections and Rheumatic Heart Disease
Streptococcal infections are common, especially among children, and they usually cause symptoms like sore throat and fever. While these infections might seem harmless, they can sometimes lead to serious complications, such as rheumatic heart disease in children.
Understanding the Link
Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) often develops as a complication of untreated strep infections. When a person gets infected with Streptococcus bacteria, the body’s immune system tries to fight off the infection. However, in some cases, the immune system attacks healthy tissues, including those in the heart, leading to long-term damage.
How Does It Happen?
If strep throat isn’t treated with antibiotics, the bacteria can trigger an immune response that causes inflammation throughout the body. This inflammation can affect the heart, leading to damage to the heart valves—a condition known as rheumatic heart disease. This is why the importance of antibiotics for strep cannot be overstated; prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications like RHD.
Recognizing Strep Throat Symptoms
Early detection is key to treating strep to prevent RHD. The typical symptoms of strep throat include:
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Swollen glands
Recognizing strep throat symptoms early and seeking medical care ensures the infection can be managed with antibiotics, minimizing the risk of rheumatic heart disease.
Early Signs of Rheumatic Heart Disease
In cases where strep throat is not treated, the development of early signs of rheumatic heart disease can occur. These signs may include:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Fatigue or weakness
- Heart palpitations
- Joint pain or swelling
These symptoms suggest that the heart might have sustained damage, which is why seeking medical attention is critical.
Complications of Strep Infections
Complications of strep infections can extend beyond the throat and affect various parts of the body, particularly the heart. When left untreated, the long-term effects of strep infections can cause permanent heart damage and valve dysfunction, significantly impacting quality of life.
Protecting Heart Health from Infections
One of the most effective ways to protect heart health from infections is to treat streptococcal infections promptly. Early intervention and the correct use of antibiotics play a crucial role in rheumatic heart disease prevention.
Rheumatic Heart Disease Prevention Tips
To avoid the severe consequences of rheumatic heart disease, consider the following prevention tips:
- Seek prompt medical attention if you experience strep throat symptoms.
- Complete the full course of antibiotics when prescribed.buy neurontin online https://bristolrehabclinic.ca/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/png/neurontin.html no prescription pharmacy
- Educate others, especially parents, on the health risks of untreated strep.
Conclusion
Streptococcal infections might seem minor, but they can lead to serious complications like rheumatic heart disease if left untreated. By recognizing the signs of strep throat and taking steps to treat the infection with antibiotics, you can significantly reduce the risk of long-term effects of strep infections. Prioritizing early intervention and understanding the health risks of untreated strep can help protect your heart from lasting damage.
To seek medical advice, always consult a Doctor. Here are our recommended experts.
Click here
To read more on Heart Disease .
Click Here