The Role of Hormones in Diagnosis and Screening for Type 1 Diabetes
Introduction: Diagnosing and screening for Type 1 diabetes is essential for early detection and effective management. Hormones play a crucial role in this process, influencing the diagnostic tests and screening methods used. In this blog, we’ll explore how hormonal imbalances contribute to the diagnosis and screening of Type 1 diabetes in simple language.
Understanding Diagnosis and Screening: Diagnosing Type 1 diabetes involves assessing blood sugar levels and other indicators of the condition. Screening aims to identify individuals at risk of developing Type 1 diabetes before symptoms appear.
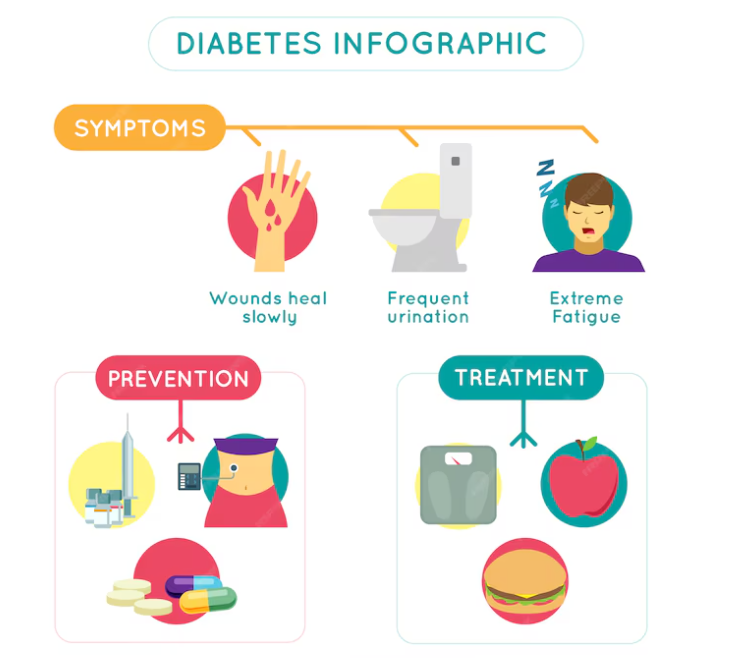
The Role of Hormones: Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, regulates blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy. In Type 1 diabetes, insulin production is deficient due to the immune system attacking and destroying insulin-producing beta cells. This hormonal imbalance leads to high blood sugar levels, a hallmark of Type 1 diabetes.
Diagnosis: Blood tests, such as fasting blood sugar tests and A1C tests, are commonly used to diagnose Type 1 diabetes. These tests measure blood sugar levels and provide insights into overall glucose control. Hormonal imbalances, particularly involving insulin, are key factors considered during the diagnostic process.
Screening: Screening for Type 1 diabetes involves assessing risk factors and conducting blood tests to identify individuals at risk of developing the condition. Hormonal imbalances, genetic predisposition, and family history are factors considered during screening. Tests such as antibody tests and genetic tests may be used to identify individuals at risk.
Understanding Imbalances: Hormonal imbalances, particularly involving insulin, contribute to the diagnosis and screening of Type 1 diabetes. High blood sugar levels resulting from insulin deficiency are indicative of the condition. Screening aims to identify individuals with hormonal imbalances and assess their risk of developing Type 1 diabetes.
Conclusion: Recognizing the role of hormones in the diagnosis and screening of Type 1 diabetes is essential for early detection and intervention. By understanding how hormonal imbalances contribute to the condition, healthcare professionals can effectively diagnose and screen individuals at risk, leading to timely treatment and improved outcomes.
To seek medical advice, always consult a Doctor. Here are our recommended experts. Click Here
To read more on Type 1 diabetes. Click Here


