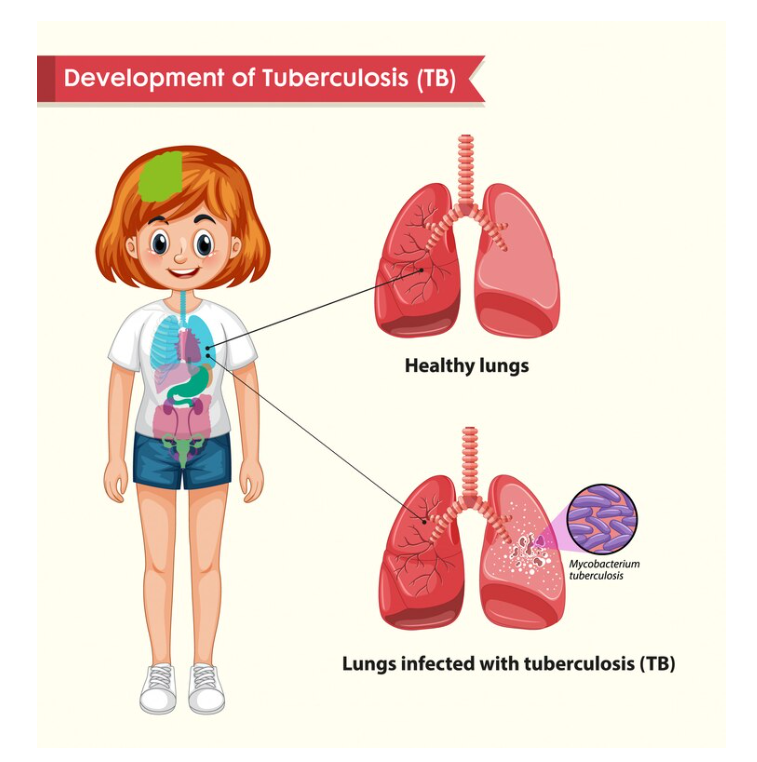
Tuberculosis in Children: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Implications
Introduction:
Tuberculosis (TB) is often thought of as a disease affecting adults, but children are also vulnerable. In this article, we’ll explore how TB manifests in children, the diagnostic process, treatment options, and potential long-term impacts.
Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Children:
Diagnosing TB in children can be tricky because their symptoms are often mild or vague. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough.
- Low-grade fever.
- Weight loss or failure to thrive.
online pharmacy buy stromectol no insurance with best prices today in the USA
- Fatigue and reduced activity levels.
To confirm TB infection, healthcare providers may use:
- Chest X-rays: To check for lung abnormalities.
- Tuberculin Skin Test (TST): Identifies an immune response to TB bacteria.
- Interferon-Gamma Release Assays (IGRAs): A blood test used to detect TB infection.
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial to prevent complications and the spread of TB.
Treatment of Tuberculosis in Children:
Children with TB require a combination of antibiotics, usually taken over six months or longer. Treatment often includes:
- Isoniazid and Rifampicin: Key drugs used to kill TB bacteria.
- Pyrazinamide and Ethambutol: Sometimes added for severe cases.
Medications are often prepared in liquid form or crushed for easier consumption. Adherence to the full course of treatment is vital to ensure recovery and prevent drug resistance. Regular follow-ups help monitor progress and address any side effects.
Long-Term Implications of Tuberculosis in Children:
Even with treatment, TB can leave lasting effects on a child’s health, particularly if there were delays in diagnosis. Potential long-term complications include:
- Lung Damage: Scarring or reduced lung function.
- Growth Issues: Stunted physical development.
- Skeletal Deformities: Particularly in cases of bone or joint TB.
Prompt intervention reduces the risk of these complications and ensures better outcomes.
Prevention and Awareness:
Preventing TB in children focuses on reducing exposure to infection and strengthening immunity. Key strategies include:
- BCG Vaccination: Offers protection against severe TB in children.
- Good Nutrition: Supports a strong immune system.
- Hygiene Practices: Minimizes exposure to TB bacteria.
- Contact Tracing: Screening household contacts of TB patients for early detection.
Educating parents, caregivers, and healthcare providers about TB symptoms and treatment is essential for early action.
Conclusion:
Tuberculosis can affect children just as it does adults, and early diagnosis and treatment are essential to protect their health. By recognizing symptoms, ensuring timely medical care, and adopting preventive measures, we can mitigate the impact of TB on children and their families.
To seek medical advice, always consult a Doctor.
Here are our recommended experts. Click here
To read more on Respiratory disease . Click Here


