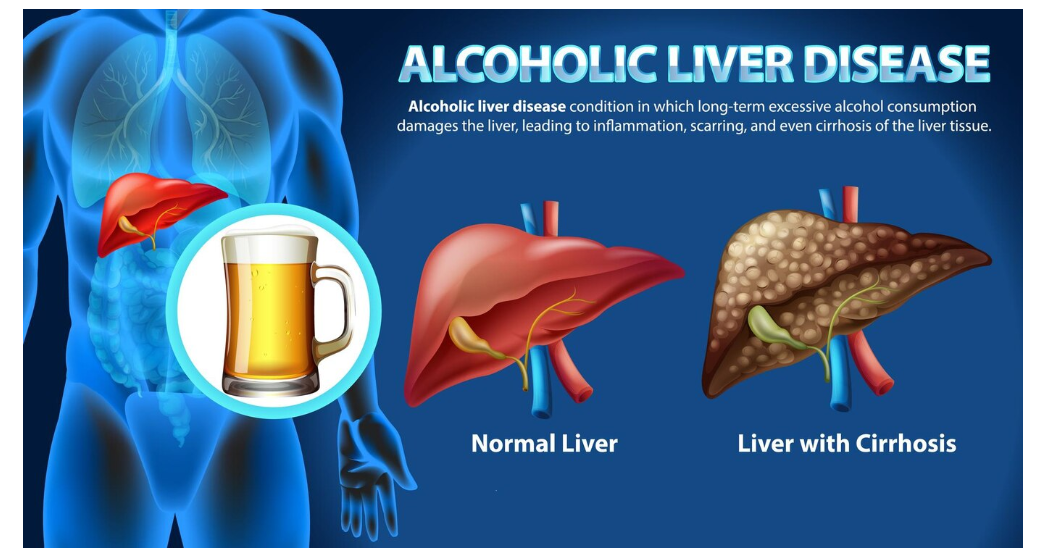
Understanding Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Exploring its Causes and Risk Factors
Introduction: You may have heard about liver diseases associated with excessive alcohol consumption, but did you know that there’s a liver condition that doesn’t require alcohol to develop? It’s called Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), and it’s more common than you might think. In this blog, we’ll delve into what NAFLD is, its causes, and the risk factors associated with it.
Understanding NAFLD: NAFLD is a condition where there’s an accumulation of fat in the liver cells, not caused by alcohol consumption. While a small amount of fat in the liver is normal, when it exceeds 5-10% of the liver’s weight, it’s considered NAFLD. This buildup of fat can lead to inflammation and scarring of the liver, affecting its ability to function properly.
Causes of NAFLD: The exact cause of NAFLD isn’t fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Overweight or Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for NAFLD. Extra fat in the body can also accumulate in the liver, leading to fatty liver disease.
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When the body becomes resistant to insulin, as is often the case in people with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome, it can lead to NAFLD.
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming a diet high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, and saturated fats can increase the risk of NAFLD. These foods contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance, both of which are linked to fatty liver disease.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Leading a sedentary lifestyle without enough physical activity can contribute to the development of NAFLD. Exercise helps burn excess fat in the liver and improves insulin sensitivity.
Risk Factors: Certain factors increase the risk of developing NAFLD, including:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Sleep apnea
- Age (NAFLD is more common in middle-aged and older adults)
Conclusion: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a common liver condition that can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. Understanding its causes and risk factors is the first step in preventing and managing NAFLD. By adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce your risk of developing NAFLD and improve your overall liver health.
To seek medical advice, always consult a Doctor. Here are our recommended experts. Click here
To read more on Respiratory disease . Click Here


